Technology Overview
18:54, 27 Oct 2021
Unity’s Data-Oriented Technology Stack was unveiled in 2017 and it offers incredible performance improvements thanks to three important innovations:
- The Entity Component System, which lays out data in the memory in a cache-friendly way.
- The Job System, which parallelizes work on multiple CPUs.
- The Burst Compiler, which generates super-fast vectorized code using LLVM.
1) Entity Component System
Data-Oriented Design
At the core of Unity DOTS is the concept of data-oriented design. Its goal is to organize data for efficient processing in order to feed data to the CPUs as fast as possible.
Cache Optimization
The processing speed of modern CPUs is so high that often the bottleneck is the bandwidth and latency between the registers of the CPU and the computer’s RAM. To counter this problem, CPUs contain several cache levels.
When the CPU needs a value, it first looks it up in the caches before trying to access it from the RAM. The closer a cache is to the registers, the faster it is to access, but the smaller its memory is.
Modern CPUs don’t access memory byte-by-byte, but rather in chunks of 64 bytes, which are called cache lines. When trying to read a particular memory location, the entire cache line is fetched, which means that accessing other values from the same cache line is fast. However, if other values in the cache line are not needed for the current computation, a cache miss occurs, which slows down the process significantly. Thus, arranging data in the memory according to its access pattern results in significantly better performance.
Entity Component System
The Entity Component System (ECS) is what applies the data-oriented design paradigm in practice by separating data from logic. It is made up of Entities, Components and Systems.
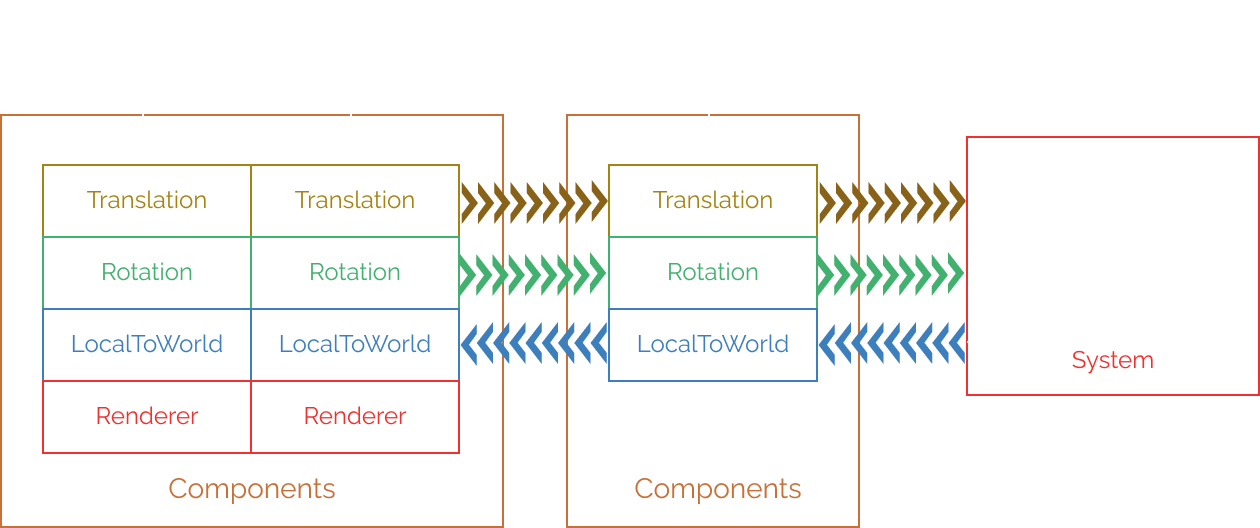
Entity
An entity is an identifier; it doesn’t store data or logic, but instead identifies which pieces of data belong together. This contrasts with traditional object-oriented programming, where each entity contains its own data.
Component
A component contains a set of data. It can be attached to an entity, which can also contain other components. Which data is stored in each component depends on how the data is accessed: if two values are always accessed together, they should generally be stored in the same component.
System
A system provides the logic that transforms component data. It usually contains the functionality of one game aspect (e.g. an hp system would add or remove hit points). Every system defines the components it needs to read and write to.
2) Jobs System
Parallelized algorithms with multi-threading have existed for a long time. However, Unity DOTS’ new Jobs System provides an interface to easily parallelize code and sync data with the main thread. It abstracts the direct thread handling from the developer and instead enqueues every job at a central scheduler, which executes it when a thread is available. Crucially, Unity has developed automatic race condition checks. Race conditions occur when one thread is writing to an array while another thread is simultaneously attempting to read the same data. They are notoriously difficult to debug.
3) Burst Compiler
A significant source of performance gain comes from optimizing code at its lowest level. Usually this means writing logic in languages like C++ or C, which can be executed directly on the processor. Thanks to the Burst Compiler, C# can be transformed into highly optimized machine code, which is designed to run natively on whichever processor a given computer is running.


 Back
Back